Fitting degradation JV data with Lazy Posterior analysis
This notebook is a demonstration of how to fit light-intensity dependent JV curves with drift-diffusion models using the SIMsalabim package.
In this example, we create synthetic JV data for a device that degrades over time, and then use Bayesian optimization to fit the data and extract the posterior distributions of the parameters using the Lazy Posterior method.
[1]:
# Import necessary libraries
import warnings, os, sys, shutil, matplotlib, ray
# remove warnings from the output
os.environ["PYTHONWARNINGS"] = "ignore"
warnings.filterwarnings(action='ignore', category=FutureWarning)
warnings.filterwarnings(action='ignore', category=UserWarning)
os.environ['PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF'] = 'expandable_segments:True'
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import default_rng
import torch, copy, uuid
import pySIMsalabim as sim
from pySIMsalabim.experiments.JV_steady_state import *
import ax, logging
from ax.utils.notebook.plotting import init_notebook_plotting, render
init_notebook_plotting() # for Jupyter notebooks
try:
from optimpv import *
from optimpv.optimizers.axBOtorch.axUtils import *
from optimpv.models.DDfits.JVAgent import JVAgent
from optimpv.optimizers.axBOtorch.axBOtorchOptimizer import axBOtorchOptimizer
from optimpv.optimizers.axBOtorch.axUtils import get_VMLC_default_model_kwargs_list
except Exception as e:
sys.path.append('../') # add the path to the optimpv module
from optimpv import *
from optimpv.optimizers.axBOtorch.axUtils import *
from optimpv.models.DDfits.JVAgent import JVAgent
from optimpv.optimizers.axBOtorch.axBOtorchOptimizer import axBOtorchOptimizer
from optimpv.optimizers.axBOtorch.axUtils import get_VMLC_default_model_kwargs_list
session_path = os.path.join(os.path.join(os.path.abspath('../'),'SIMsalabim','SimSS'))
[INFO 01-20 11:52:31] ax.utils.notebook.plotting: Injecting Plotly library into cell. Do not overwrite or delete cell.
[INFO 01-20 11:52:31] ax.utils.notebook.plotting: Please see
(https://ax.dev/tutorials/visualizations.html#Fix-for-plots-that-are-not-rendering)
if visualizations are not rendering.
Define the parameters for the simulation
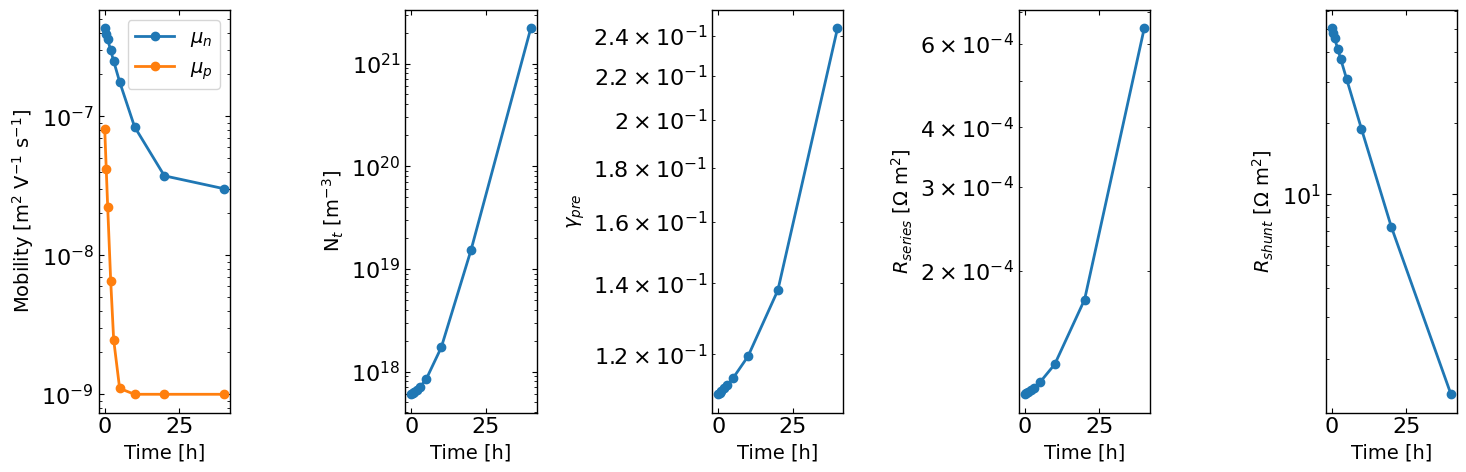
Here we will simulate a degradation type experiment where the hole mobility, bulk trap density, preLangevin factor, series resistance and shunt resistance change over time. We can then investigate how well we can recover the time-dependent parameters and their “Lazy posterior” distributions.
[2]:
times = np.asarray([0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5, 10, 20, 40]) # time points for transient simulations
mun_list = 4e-7 * np.exp(-times/5) + 3e-8 # time-dependent electron mobility
mup_list = 8e-8 * np.exp(-times/1.5)**2 + 1e-9 # time-dependent hole mobility
bulk_tr_list = 1e17 * np.exp(times/4) + 5e17 # time-dependent bulk trap density
preLangevin_list = 0.01 * np.exp(times/15) + 0.1 # time-dependent preLangevin factor
R_series_list = 1e-5 * np.exp(times/10) + 1e-4 # time-dependent series resistance
R_shunt_list = 0.5e2 * np.exp(-times/10) + 5e-1 # time-dependent shunt resistance
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,5, figsize=(15,5))
axes[0].plot(times, mun_list, 'o-')
axes[0].plot(times, mup_list, 'o-')
axes[0].set_yscale('log')
axes[0].set_xlabel('Time [h]')
axes[0].legend([r'$\mu_n$', r'$\mu_p$'])
axes[0].set_ylabel('Mobility [m$^2$ V$^{-1}$ s$^{-1}$]')
axes[1].plot(times, bulk_tr_list, 'o-')
axes[1].set_yscale('log')
axes[1].set_xlabel('Time [h]')
axes[1].set_ylabel(r'N$_t$ [m$^{-3}$]')
axes[2].plot(times, preLangevin_list, 'o-')
axes[2].set_yscale('log')
axes[2].set_xlabel('Time [h]')
axes[2].set_ylabel(r'$\gamma_{pre}$')
axes[3].plot(times, R_series_list, 'o-')
axes[3].set_yscale('log')
axes[3].set_xlabel('Time [h]')
axes[3].set_ylabel(r'$R_{series}$ [$\Omega$ m$^2$]')
axes[4].plot(times, R_shunt_list, 'o-')
axes[4].set_yscale('log')
axes[4].set_xlabel('Time [h]')
axes[4].set_ylabel(r'$R_{shunt}$ [$\Omega$ m$^2$]')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
[3]:
def make_data(times, mun_list, mup_list, bulk_tr_list, preLangevin_list, R_series_list, R_shunt_list):
# Set the session path for the simulation and the input files
session_path = os.path.join(os.path.join(os.path.abspath('../'),'SIMsalabim','SimSS'))
input_path = os.path.join(os.path.join(os.path.join(os.path.abspath('../'),'Data','simsalabim_test_inputs','fakeOPV')))
simulation_setup_filename = 'simulation_setup_fakeOPV.txt'
simulation_setup = os.path.join(session_path, simulation_setup_filename)
# path to the layer files defined in the simulation_setup file
l1 = 'ZnO.txt'
l2 = 'ActiveLayer.txt'
l3 = 'BM_HTL.txt'
l1 = os.path.join(input_path, l1)
l2 = os.path.join(input_path, l2)
l3 = os.path.join(input_path, l3)
# copy this files to session_path
force_copy = True
if not os.path.exists(session_path):
os.makedirs(session_path)
for file in [l1,l2,l3,simulation_setup_filename]:
file = os.path.join(input_path, os.path.basename(file))
if force_copy or not os.path.exists(os.path.join(session_path, os.path.basename(file))):
shutil.copyfile(file, os.path.join(session_path, os.path.basename(file)))
else:
print('File already exists: ',file)
dic_res = {}
print('Generating data for times: ', times)
for i, t in enumerate(times):
params = [] # list of parameters to be optimized
mup = FitParam(name = 'l2.mu_p', value = mup_list[i], bounds = [5e-10,1e-6], log_scale = True, value_type = 'float', fscale = None, rescale = False, display_name=r'$\mu_p$', unit=r'm$^2$ V$^{-1}$s$^{-1}$', axis_type = 'log', force_log = True)
params.append(mup)
mun = FitParam(name = 'l2.mu_n', value = mun_list[i], bounds = [5e-10,1e-6], log_scale = True, value_type = 'float', fscale = None, rescale = False, display_name=r'$\mu_n$', unit='m$^2$ V$^{-1}$s$^{-1}$', axis_type = 'log', force_log = True)
params.append(mun)
bulk_tr = FitParam(name = 'l2.N_t_bulk', value = bulk_tr_list[i], bounds = [1e17,1e22], log_scale = True, value_type = 'float', fscale = None, rescale = False, display_name=r'$N_{T}$', unit=r'm$^{-3}$', axis_type = 'log', force_log = True)
params.append(bulk_tr)
preLangevin = FitParam(name = 'l2.preLangevin', value = preLangevin_list[i], bounds = [0.005,1], log_scale = True, value_type = 'float', fscale = None, rescale = False, display_name=r'$\gamma_{pre}$', unit=r'-', axis_type = 'log', force_log = True)
params.append(preLangevin)
R_series = FitParam(name = 'R_series', value = R_series_list[i], bounds = [1e-5,1e-1], log_scale = True, value_type = 'float', fscale = None, rescale = False, display_name=r'$R_{series}$', unit=r'$\Omega$ m$^2$', axis_type = 'log', force_log = True)
params.append(R_series)
R_shunt = FitParam(name = 'R_shunt', value = R_shunt_list[i], bounds = [1e-2,1e2], log_scale = True, value_type = 'float', fscale = None, rescale = False, display_name=r'$R_{shunt}$', unit=r'$\Omega$ m$^2$', axis_type = 'log', force_log = True)
params.append(R_shunt)
# reset simss
# Set the JV parameters
Gfracs = [0.1,0.5,1.0] # Fractions of the generation rate to simulate (None if you want only one light intensity as define in the simulation_setup file)
UUID = str(uuid.uuid4()) # random UUID to avoid overwriting files
cmd_pars = [] # see pySIMsalabim documentation for the command line parameters
# Add the parameters to the command line arguments
for param in params:
cmd_pars.append({'par':param.name, 'val':str(param.value)})
# Run the JV simulation
ret, mess = run_SS_JV(simulation_setup, session_path, JV_file_name = 'JV.dat', G_fracs = Gfracs, parallel = True, max_jobs = 3, UUID=UUID, cmd_pars=cmd_pars)
# save data for fitting
X,y = [],[]
X_orig,y_orig = [],[]
if Gfracs is None:
data = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(session_path, 'JV_'+UUID+'.dat'), sep=r'\s+') # Load the data
Vext = np.asarray(data['Vext'].values)
Jext = np.asarray(data['Jext'].values)
G = np.ones_like(Vext)
rng = default_rng()#
noise = rng.standard_normal(Jext.shape) * 0.01 * Jext
Jext = Jext + noise
X = Vext
y = Jext
else:
for Gfrac in Gfracs:
data = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(session_path, 'JV_Gfrac_'+str(Gfrac)+'_'+UUID+'.dat'), sep=r'\s+') # Load the data
Vext = np.asarray(data['Vext'].values)
Jext = np.asarray(data['Jext'].values)
G = np.ones_like(Vext)*Gfrac
rng = default_rng()#
noise = 0 #rng.standard_normal(Jext.shape) * 0.005 * Jext
if len(X) == 0:
X = np.vstack((Vext,G)).T
y = Jext + noise
y_orig = Jext
else:
X = np.vstack((X,np.vstack((Vext,G)).T))
y = np.hstack((y,Jext+ noise))
y_orig = np.hstack((y_orig,Jext))
# remove all the current where Jext is higher than a given value
X = X[y<200]
X_orig = copy.deepcopy(X)
y_orig = y_orig[y<200]
y = y[y<200]
masks = []
for Gfrac in Gfracs:
mask = y[X[:,1]==Gfrac] < 200
masks.append(mask)
# Find the minimum number of valid points across all G fractions
min_points = min(np.sum(mask) for mask in masks)
# Apply consistent filtering: keep only the first min_points for each G fraction
X_filtered = []
y_filtered = []
y_orig_filtered = []
for i, Gfrac in enumerate(Gfracs):
Gfrac_indices = np.where(X[:,1]==Gfrac)[0]
valid_indices = Gfrac_indices[masks[i]][:min_points]
X_filtered.append(X[valid_indices])
y_filtered.append(y[valid_indices])
y_orig_filtered.append(y_orig[valid_indices])
X = np.vstack(X_filtered)
y = np.hstack(y_filtered)
y_orig = np.hstack(y_orig_filtered)
X_orig = copy.deepcopy(X)
# reshape y such that each Gfrac is a column
y_reshaped = y.reshape((len(Gfracs), int(len(y)/len(Gfracs))))
# The following calculates sigma using a similar approach as in Eunchi Kim et al. DOI: 10.1002/solr.202500648
# calculate the sigma for the experimental data
std_phi = 0.05 # 5% error on light intensity
std_vol = 0.01 # 10 mV error on voltage
# get dy/dGfrac
dJ_dphi = np.gradient(y_reshaped,Gfracs,axis=0,edge_order=2)
dJ_dV = np.gradient(y_reshaped,X[:,0][X[:,1]==Gfracs[0]],axis=1,edge_order=2)
phi_term = (std_phi * dJ_dphi)**2
vol_term = (std_vol * dJ_dV)**2
phi_term = phi_term.flatten()
vol_term = vol_term.flatten()
sigma_J = np.sqrt((std_phi*dJ_dphi)**2 + (std_vol*dJ_dV)**2)
sigma_J = sigma_J.flatten() # convert to absolute error
dic_res[t] = {'X':X, 'y':y, 'sigma_J':sigma_J, 'params':params}
return dic_res
dic_data = make_data(times, mun_list, mup_list, bulk_tr_list, preLangevin_list, R_series_list, R_shunt_list)
Generating data for times: [ 0. 0.5 1. 2. 3. 5. 10. 20. 40. ]
[4]:
plt.figure()
for _ in dic_data.keys():
data = dic_data[_]
X = data['X']
y = data['y']
plt.plot(X[X[:,1]==1.0,0],y[X[:,1]==1.0],label='t = '+str(_)+' s, Gfrac = 1.0')
plt.xlabel('Voltage [V]')
plt.ylabel('Current density [A/m$^2$]')
plt.show()

[5]:
# Initialize Ray – ensure this runs only once
if not ray.is_initialized():
ray.init(ignore_reinit_error=True, num_cpus=180)
@ray.remote
def run_single_chain(params, jv, num_free_params):
"""Run a single optimization chain and return ax_client.summarize()."""
optimizer = axBOtorchOptimizer(
params=params,
agents=jv,
models=['SOBOL','BOTORCH_MODULAR'],
n_batches=[5,100],
batch_size=[5,2],
ax_client=None,
max_parallelism=-1,
model_kwargs_list=get_VMLC_default_model_kwargs_list(
num_free_params=num_free_params
),
model_gen_kwargs_list=None,
name='ax_opti',
parallel=True,
verbose_logging=False
)
optimizer.optimize_turbo(acq_turbo='ts')
return optimizer.ax_client.summarize()
@ray.remote
def run_single_k(k, entry):
"""Run all optimization for a single dictionary entry (one device)."""
params = entry['params']
X = entry['X']
y = entry['y']
sigma_J = entry['sigma_J']
num_free_params = len([p for p in params if p.type != 'fixed'])
# ---- Setup SIMsalabim paths ----
session_path = os.path.join(os.path.abspath('../'), 'SIMsalabim', 'SimSS')
input_path = os.path.join(os.path.abspath('../'), 'Data','simsalabim_test_inputs','fakeOPV')
simulation_setup_filename = 'simulation_setup_fakeOPV.txt'
simulation_setup = os.path.join(session_path, simulation_setup_filename)
# ---- Metrics for optimization ----
metric = 'nrmse'
loss = 'linear'
tracking_metrics = 'LLH'
tracking_loss = 'linear'
tracking_weight = 1 / sigma_J**2
jv = JVAgent(
params, X, y,
session_path,
simulation_setup,
parallel=True,
max_jobs=1,
metric=metric,
loss=loss,
tracking_metric=tracking_metrics,
tracking_loss=tracking_loss,
tracking_weight=tracking_weight,
tracking_X=X,
tracking_y=y,
tracking_exp_format='JV'
)
# ---- Launch 10 optimization chains in parallel ----
futures = [
run_single_chain.remote(params, jv, num_free_params)
for _ in range(10)
]
results = ray.get(futures)
# Concatenate all dataframes
data_main = pd.concat(results, ignore_index=True)
# return a tuple to rebuild the dictionary
return (k, data_main)
def run_fit(dic):
"""Ray-distributed full optimization over all dictionary entries."""
futures = [
run_single_k.remote(k, dic[k])
for k in dic.keys()
]
results = ray.get(futures)
# Update dic with results
for k, data in results:
dic[k]['data_main'] = data
return dic
2026-01-20 11:52:39,673 INFO worker.py:2014 -- Started a local Ray instance. View the dashboard at http://127.0.0.1:8265
(run_single_chain pid=1634757) [WARNING 01-20 11:55:45] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634809) [WARNING 01-20 11:56:15] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634751) [WARNING 01-20 11:56:34] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634775) [WARNING 01-20 11:56:44] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634840) [WARNING 01-20 11:56:51] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634744) [WARNING 01-20 11:56:58] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 3x across cluster] (Ray deduplicates logs by default. Set RAY_DEDUP_LOGS=0 to disable log deduplication, or see https://docs.ray.io/en/master/ray-observability/user-guides/configure-logging.html#log-deduplication for more options.)
(run_single_chain pid=1634801) [WARNING 01-20 11:57:10] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 3x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634802) [WARNING 01-20 11:57:18] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634805) [WARNING 01-20 11:57:20] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634760) [WARNING 01-20 11:57:27] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 5x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634784) [WARNING 01-20 11:57:39] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 2x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634803) [WARNING 01-20 11:57:46] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 4x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634796) [ERROR 01-20 11:58:06] optimpv.axBOtorchOptimizer: Error in Turbo batch 83: All attempts to fit the model have failed.
(run_single_chain pid=1634796) [ERROR 01-20 11:58:06] optimpv.axBOtorchOptimizer: We are stopping the optimization process
(run_single_chain pid=1634796) [WARNING 01-20 11:58:06] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634839) [WARNING 01-20 11:58:07] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634814) [WARNING 01-20 11:58:14] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 3x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634756) [WARNING 01-20 11:58:25] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 3x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634770) [WARNING 01-20 11:58:35] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 2x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634748) [WARNING 01-20 11:58:42] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 2x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634824) [WARNING 01-20 11:58:47] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634806) [WARNING 01-20 11:58:49] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634798) [WARNING 01-20 11:58:58] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 5x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634792) [WARNING 01-20 11:59:03] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 3x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634746) [WARNING 01-20 11:59:09] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 4x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634754) [WARNING 01-20 11:59:20] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 2x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634750) [WARNING 01-20 11:59:27] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 8x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634808) [WARNING 01-20 11:59:32] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 5x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634734) [WARNING 01-20 11:59:37] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 5x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634733) [WARNING 01-20 11:59:49] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 5x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634743) [WARNING 01-20 11:59:55] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634795) [WARNING 01-20 11:59:58] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric.
(run_single_chain pid=1634817) [WARNING 01-20 12:00:04] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 5x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634819) [WARNING 01-20 12:00:14] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 6x across cluster]
(run_single_chain pid=1634843) [WARNING 01-20 12:00:27] ax.api.client: Metric IMetric('JV_JV_LLH_linear') not found in optimization config, added as tracking metric. [repeated 2x across cluster]
[6]:
%%time
dic_data = run_fit(dic_data)
CPU times: user 3.41 s, sys: 1.21 s, total: 4.62 s
Wall time: 7min 46s
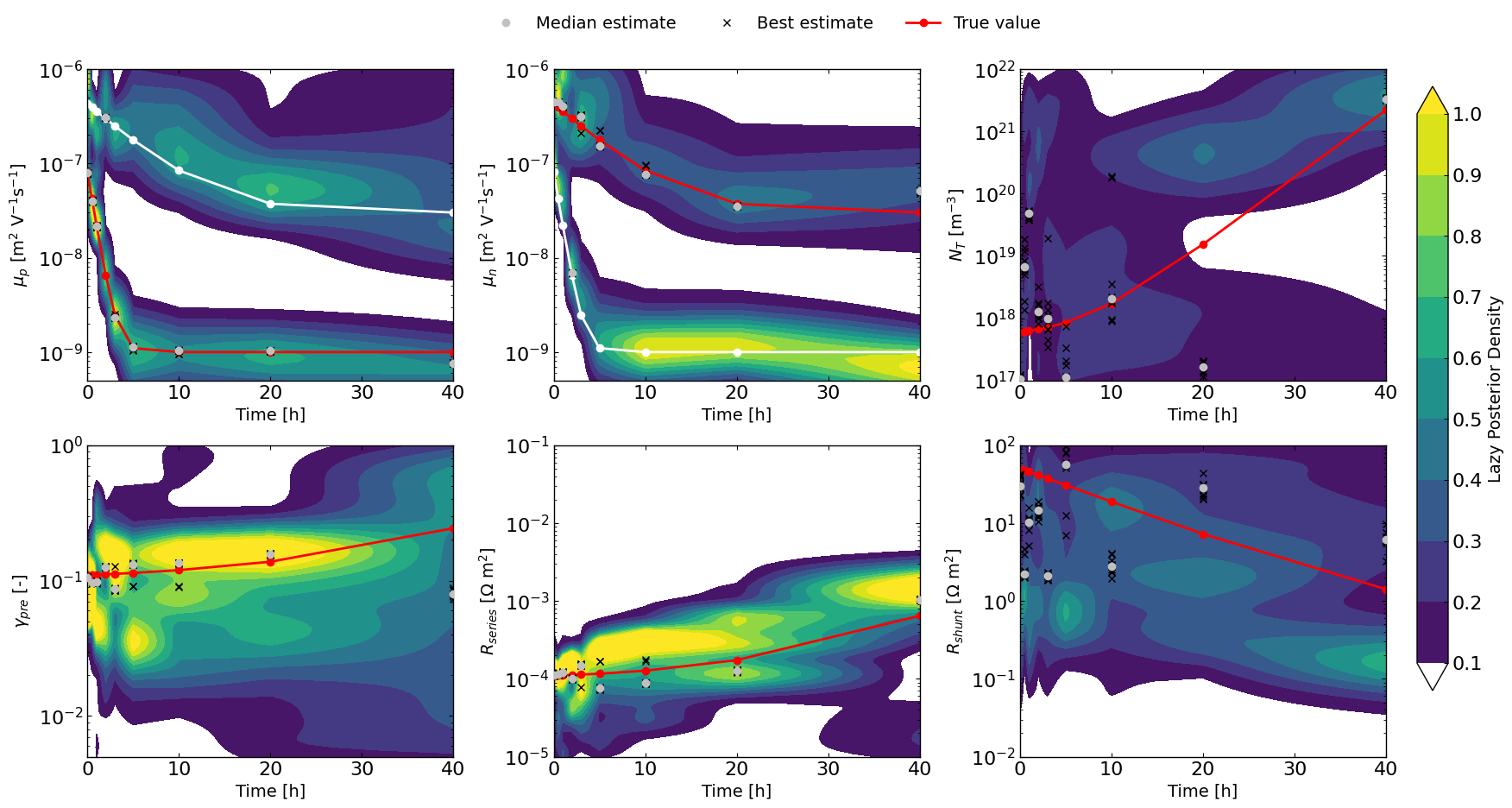
The “lazy” posterior
The following implementation has NO mathematical support as far as I (VMLC) knows, but I will make the following argument.
One could think of each Bayesian Optimization run using TuRBO as similar to a different chain in a classical MCMC approach.
In that analogy, the random sampling first step for the BO would be equivalent to the warm-up stage in MCMC which can therefore be discarded. The TURBO stage would be equivalent to the normal chain path.
Therefore if we were to looks at the density of point that gets explored during the TURBO stage for multiple “chains” we would expect to get something that is not too different from doing MCMC.
To explore this, the LazyPosterior class has been implemented and shows promising results.
[7]:
from optimpv.posterior.lazy_posterior import LazyPosterior
viridis = plt.get_cmap('viridis', len(dic_data.keys()))
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2,3, figsize=(18,10))
ax_ = axes.flatten()
for idx_par in range(len(dic_data[0]['params'])): # 0: mup, 1: mun, 2: bulk_tr, 3: preLangevin, 4: R_series, 5: R_shunt
kde_2d = []
median_pars,top10 = [], []
for _ in dic_data.keys():
outcome_name = 'JV_JV_LLH_linear' #optimizer.all_tracking_metrics[0] #'LLH'
data_main = dic_data[_]['data_main']
data_main = data_main[data_main['trial_index']>=30] # discard the random sampling part
params = dic_data[_]['params']
lazy_post = LazyPosterior(params, data_main, outcome_name)
par_name = params[idx_par].name
par_log_scale = params[idx_par].log_scale or params[idx_par].force_log
kde_ = lazy_post._compute_1D_kde(par_name, log_scale=par_log_scale)
params_median = lazy_post.get_top_n_metrics_params('median', num=10)
top10_params = lazy_post.get_top_n_best_params(num=10)
top10.append([val[idx_par].value for val in top10_params])
# calculate the median of the top 10 params
median_pars.append(params_median[idx_par].value)
bounds = params[idx_par].bounds
if par_log_scale:
par_x = np.logspace(np.log10(bounds[0]), np.log10(bounds[1]), 100)
else:
par_x = np.linspace(bounds[0], bounds[1], 100)
kde_2d.append((par_x,kde_(par_x)))
# make a grid for times
times_grid = np.array(list(dic_data.keys()))
X_, Y_ = np.meshgrid(times_grid, kde_2d[0][0])
Z = np.zeros_like(X_)
for i, t in enumerate(times_grid):
kde_vals = kde_2d[i][1]
Z[:,i] = kde_vals
# Choose a base colormap
vmin = 0.1
vmax = 1.0
cmap = matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap('viridis').copy()
# Set the color for values below the threshold
cmap.set_under("white")
# last viridis color for values above vmax
cmap.set_over(cmap.colors[-1])
# Levels: start at threshold
levels = np.linspace(vmin, vmax, 10)
cp = ax_[idx_par].contourf(X_, Y_, Z, levels=levels, cmap=cmap,extend='both')
ax_[idx_par].plot(times, median_pars, 'o', color='silver', label='Median estimate',zorder=6)
top10=np.asarray(top10)
for i in range(len(times)):
ax_[idx_par].plot(times, top10[:,i], 'x', color='black', label='Best estimate' if i == 0 else "",zorder=4)
if idx_par == 1 or idx_par == 0:
ax_[idx_par].plot(times, mun_list, 'w-o' if idx_par==0 else 'r-o', label=r'$\mu_n$ true')
ax_[idx_par].plot(times, mup_list, 'w-o' if idx_par==1 else 'r-o', label=r'$\mu_p$ true')
else:
true_vals = {
2: bulk_tr_list,
3: preLangevin_list,
4: R_series_list,
5: R_shunt_list
}
ax_[idx_par].plot(times, true_vals[idx_par], 'r-o', label='True value')
ax_[idx_par].set_ylim(bounds)
# plt.colorbar(cp, ax=ax_[idx_par])
ax_[idx_par].set_xlabel('Time [h]')
ax_[idx_par].set_ylabel(params[idx_par].full_name)
ax_[idx_par].set_yscale('log' if params[idx_par].log_scale or params[idx_par].force_log else 'linear')
# set one main colorbar for all subplots
plt.tight_layout()
fig.subplots_adjust(right=0.9, top=0.87)
cbar_ax = fig.add_axes([0.92, 0.15, 0.02, 0.7])
cbar = fig.colorbar(cp, cax=cbar_ax)
cbar.set_label('Lazy Posterior Density')
# add one legend for all subplots
handles, labels = ax_[-1].get_legend_handles_labels()
fig.legend(handles, labels, loc='upper center', bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, 0.95), ncol=3,frameon=False)
plt.show()
[8]:
# Clean up the output files (comment out if you want to keep the output files)
sim.clean_all_output(session_path)
sim.delete_folders('tmp',session_path)
# uncomment the following lines to delete specific files
sim.clean_up_output('ZnO',session_path)
sim.clean_up_output('ActiveLayer',session_path)
sim.clean_up_output('BM_HTL',session_path)
sim.clean_up_output('simulation_setup_fakeOPV',session_path)